The interventional radiology is a rapidly advancing branch of medicine. It is the radiology department that performs surgical treatments without the surgery, accompanied by imaging methods such as angiography, ultrasound, especially vascular and tumor diseases.
The interventional radiology does not deal with a single subject or organ system, such as skin diseases or heart diseases. It performs the previous surgical treatments of many organ systems without surgery.
The main features in the interventional radiology treatments are that there is no need for the surgery and narcosis. The procedures are always done with a small pinhole insertion. After the procedures, there is no trace on the body. For this reason, they are also called minimal surgical procedures. Since the imaging methods are always used when entering the body, there is a chance to see inside the body and perform treatment without cutting the skin and without damaging the target organ.
In the vast majority of procedures, the patient is sent to home on the same day or after a maximum of one day of hospitalization.
It is mostly high-tech devices that are used in the therapeutic procedures of the patients.
What is the advantage of being treated by the interventional radiology specialist?
In order to become an interventional radiologist, it is necessary to first be a radiologist, that is, to have a diploma in diagnosis, and then to have at least 5 years of experience in the interventional both during and after the residency. The radiologists are the only experts in the imaging such as vascular or ultrasound, CT, MRI, and they have extensive knowledge and the ability to use these devices in detail.
Successfully performing interventional procedures is possible by accurately and quickly detecting which vessel or organ is diseased and which is normal, and by using these devices at the highest level.
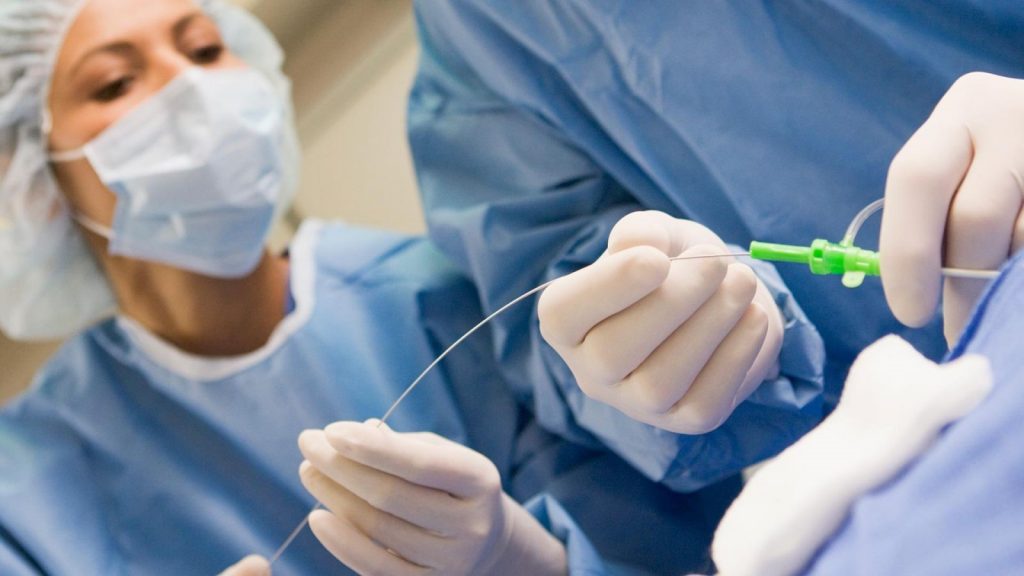
Interventional Radiological Procedures
Angiography: It is X-ray examination of the artery or vein. It is the visualization of the veins by administering contrast material after the vein is entered.
Balloon angioplasty and stent: It is the opening of occluded or narrowed vessels by advancing a balloon catheter or stent into the vessel.
Embolization: It is intravenous occlusion of the bleeding vessel, bubble, or tumor.
Chemoembolization: It is the direct administration of drugs to the cancer cells by intravenous route.
Dialysis interventions: It is opening of the fistula stenosis and occlusion, and insertion of permanent catheter.
It is the opening of the vessels with angiography for the treatment of non-healing wounds in the diabetes patients.
Radiofrequency / Microwave ablation: It is the use of radiofrequency energy to kill the cancer cells.
Thrombolysis: It is the opening of the clogged vessel by giving a clot-dissolving drug.
Transjugular intrahepatic portal-systemic shunt: It is a procedure for reducing portal hypertension and harmful effects in severe liver failure.

