

Carotid artery occlusion (Carotid vessel stenosis)
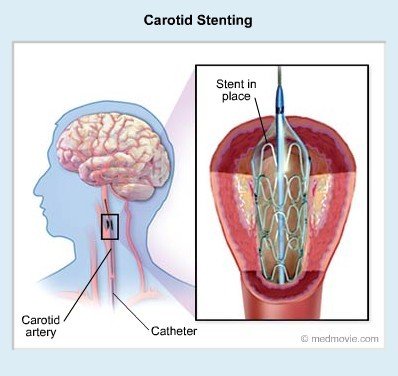
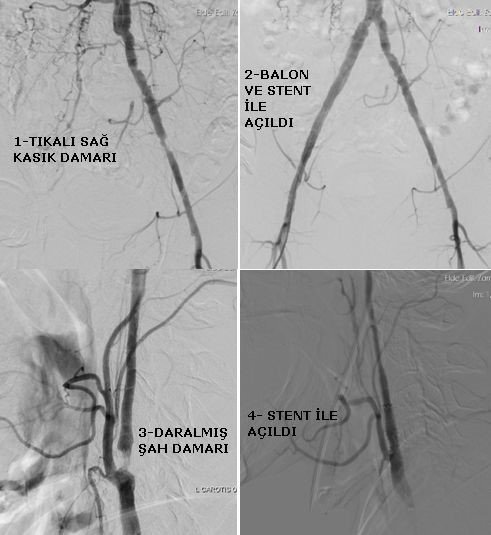
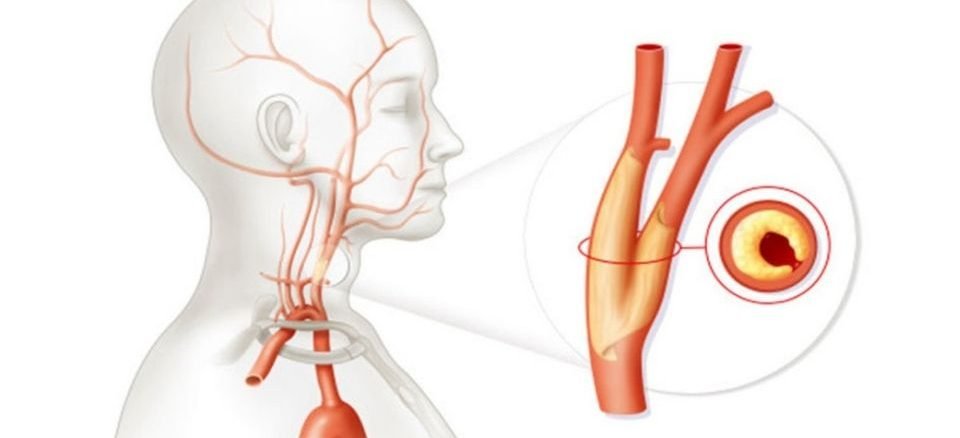
The carotid artery, which is the main vein that feeds our brain, is a vein that is very affected by occlusion and blockages due to hardening of the arteries. In case of occlusion-occlusion of the carotid artery, temporary paralysis, loss of vision, inability to speak, very serious permanent paralysis and even loss of life can occur due to insufficient blood supply to the brain or due to particles breaking off from the stenosis and going to the brain. Color ultrasound imaging with doppler ultrasound is usually sufficient to detect this disorder, which can have very negative consequences, but other radiological methods, CT-angio or MR-angio, can be used to determine the degree of stenosis and to guide the treatment. Stenosis in the neck artery can cause blood clots to form in the brain and cause a stroke. If the occlusion is mild, that is, if there is less than 70% occlusion in the vessel, the risk is low and drug treatment is sufficient. If the occlusion of the neck artery is more than 70%, the probability of a clot to the brain is higher and the stenosis usually needs to be corrected or removed. In the patients who are suitable for intravenous treatment, stenosis is shown during angiography, and then a special filter is placed to reduce the possibility of fragments leaking into the brain during the procedure, and then the stenosis is opened with safe stent and balloon applications. The patient returns to bed immediately after the procedure and is discharged after an overnight hospital stay.