Myoma embolization
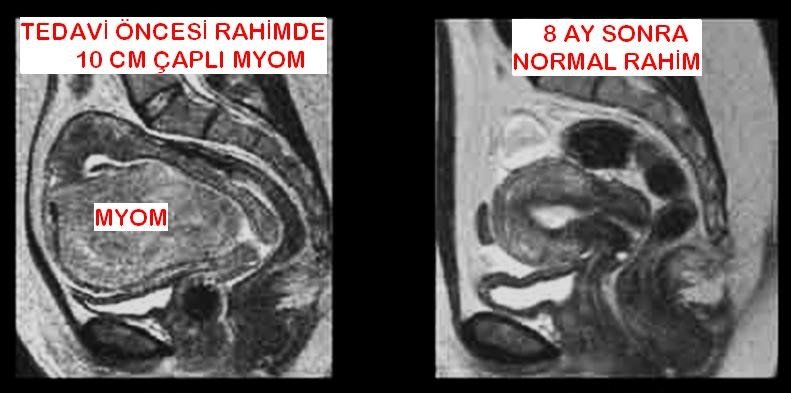
Myoma is a benign tumor originating from the uterine tissue. Their diameter can usually be between 1 and 20 cm. Myomas are the most common tumors of the female reproductive organs. Myomas are found in one out of every three women over the age of 35. Estrogen, which is known as the female hormone, causes myomas to grow. For this reason, myomas usually grow about more during reproductive age and pregnancy, and usually shrink at menopause. When it grows and causes complaints, it requires treatment. If it is small and not complaining, it can only be followed.
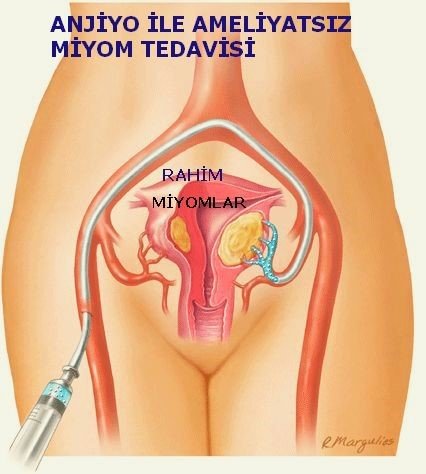
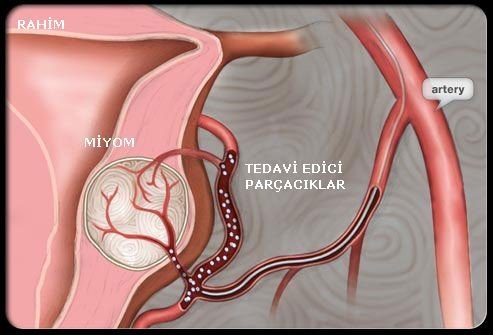
Myoma embolization is a non-surgical treatment of myomas and has been performed for about 20 years. The most important advantage is that it protects the uterus. The procedure is done by angiography. It does not require narcosis. Patients are usually discharged after a one-day hospital stay. Myomas are multi-vascular tumors. It is fed by the cervix. When the uterine vessels are blocked, myomas cannot be fed and shrink. Occlusion of the uterine vessel does not harm the uterus, because the uterus continues to be fed from many points. In scientific studies, treatment of myomas with embolization has a similar effect when compared to surgical removal.